PAPAS Team Travels to South Africa for Nematology Symposium
Three PAPAS researchers recently traveled to South Africa to meet with nematologists from around the world.

Three PAPAS researchers recently traveled to South Africa to meet with nematologists from around the world.

Evaluating the total effect of litchi tomato plant biomass compounds for root-knot nematode management.

Researching the potential for breeding PCN-resistant russet varieties, an important step toward developing more PCN-resistant potato varieties for a stronger potato industry.

Nematologists and plant pathologists gather to learn what’s new in potato nematode diagnostics.
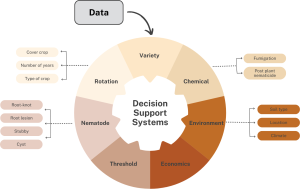
Providing potato growers with precise, data-driven strategies to effectively and sustainably combat plant-parasitic nematodes.

Watch our free webinar to see the latest discoveries in potato nematode control, detection, and resistant variety development.

The PAPAS 2024 annual report showcases significant progress made in research for systems approach to potato nematode management.

Learn more about why sampling for nematodes is important for potatoes; consideration for soil sampling (number of samples, depth, time of year); and research about potato nematode presence and sampling.

Advancing potato varieties with resistance to Columbia root-knot nematode (CRKN) through genomic prediction.

Developing a potato cultivar that is resistant to both Potato Virus Y (PVY) and potato cyst nematodes.