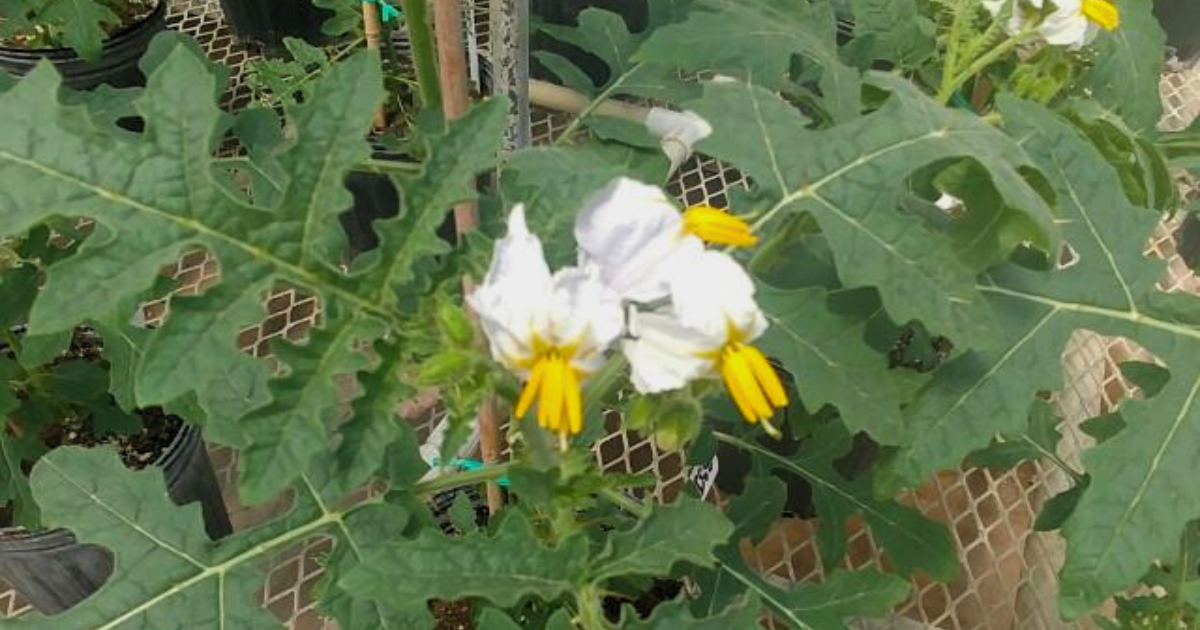
Litchi tomato for Control of Potato Nematodes
Solanum sisymbriifolium, also known as litchi tomato or sticky nightshade, is one of the promising feedstocks for nematicides production. Solanum sisymbriifolium has been shown to be efficient for the control of potato nematodes such as Globodera rostochiensis and Globodera pallida. This makes S. sisymbriifolium a valuable alternative method to control nematodes without relying on synthetic chemical nematicides, which can have harmful effects on the environment and human health.

The nematocidal action is attributed to the chemicals naturally produced by S. sisymbriifolium. Roots and shoots of S. sisymbriifolium contain several biologically active chemical compounds such as solamargine glycoalkaloid. Using different solvents and extraction techniques, the exact chemical composition of S. sisymbriifolium is being investigated. Once the most promising nematicide is identified, a potential formulation will be evaluated. Potential nematocidal compounds are being tested for their activity.