Columbia Root-Knot Nematode Impact on Potato
Found in the western US, Columbia root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne chitwoodi) infects potato roots and tubers, causing blemishes and defects that reduce quality.

Found in the western US, Columbia root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne chitwoodi) infects potato roots and tubers, causing blemishes and defects that reduce quality.

Widespread across cooler climates, northern root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne hapla) causes internal and external tuber damage that reduces potato quality.

PAPAS is studying litchi tomato (Solanum sisymbriifolium) for the plant’s genetic immunity to several potato nematode species.

PAPAS is developing computational tools with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to support potato nematode detection, mitigation, and management.

Developing molecular markers of Columbia root-knot nematode (M. Chitwoodi) aids in faster identification of the potato nematode races.

Root lesion nematodes destructively feed on plant cells, causing massive root tissue necrosis, and are linked to the spread of pathogens.
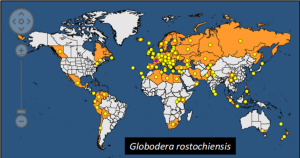
Pale cyst nematode (G. pallida) is found 49 countries/regions and golden nematode (G. rostochiensis) is found in 74 countries/regions as of 2022.

Information about the life cycle and spread of potato cyst nematodes (Globadera spp.).

How PAPAS sets up field trial microplots in Idaho to research pale cyst nematode, a regulated potato pest.